Quick reference for the WiPy¶
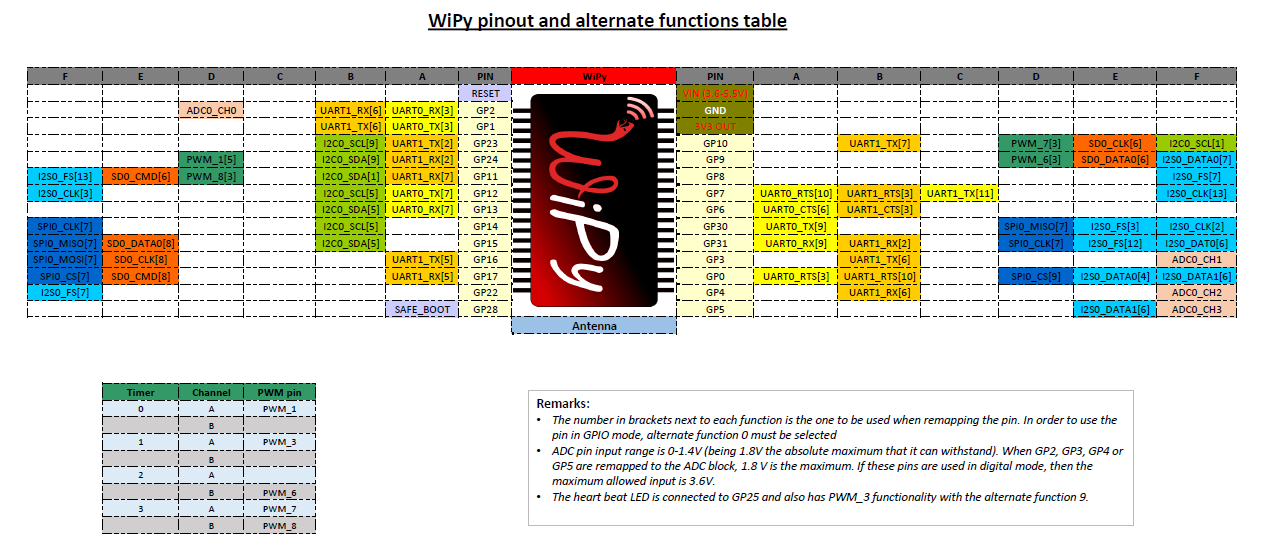
General board control¶
See pyb.
import pyb
help(pyb) # display all members from the pyb module
pyb.delay(50) # wait 50 milliseconds
pyb.millis() # number of milliseconds since boot-up
pyb.freq() # get the CPU frequency
pyb.unique_id() # return the 6-byte unique id of the board (the WiPy's MAC address)
Pins and GPIO¶
See pyb.Pin.
from pyb import Pin
# initialize GP2 in gpio mode (af=0) and make it an output
p_out = Pin('GP2', af=0, mode=Pin.OUT)
p_out.high()
p_out.low()
p_out.toggle()
# make GP1 an input with the pull-up enabled
p_in = Pin('GP1', af = 0, mode=Pin.IN, type = Pin.STD_PU)
p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1
Timers¶
from pyb import Timer
from pyb import Pin
tim = Timer(1, mode=Timer.PERIODIC)
tim_a = tim.channel(Timer.A, freq=1000)
tim_a.time() # get the value in microseconds
tim_a.freq(1) # 1 Hz
p_out = Pin('GP2', af=0, mode=Pin.OUT)
tim_a.callback(handler=lambda t: p_out.toggle())
PWM (pulse width modulation)¶
from pyb import Timer
from pyb import Pin
# assign GP25 to alternate function 5 (PWM)
p_out = Pin('GP25', af=9, type=Pin.STD)
# timer 2 in PWM mode and width must be 16 buts
tim = Timer(2, mode=Timer.PWM, width=16)
# enable channel A @1KHz with a 50% duty cycle
tim_a = tim.channel(Timer.A, freq=1000, duty_cycle=50)
ADC (analog to digital conversion)¶
See pyb.ADC.
from pyb import ADC
adc = ADC(1)
adc.read() # read value, 0-4095
UART (serial bus)¶
from pyb import Pin, UART
# first assign TX and RX to the correct pins
Pin('GP1', af=3, mode=Pin.STD_PU) # TX
Pin('GP2', af=3, mode=Pin.STD_PU) # RX
uart = UART(1, 9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes
SPI bus¶
from pyb import Pin, SPI
# first assign CLK, MISO, MOSI, CS to the correct pins
Pin('GP14', af=7, mode=Pin.STD) # CLK
Pin('GP15', af=7, mode=Pin.STD) # MISO
Pin('GP16', af=7, mode=Pin.STD) # MOSI
Pin('GP17', af=7, mode=Pin.STD) # NSS/CS
# configure the SPI master @ 2MHz
spi = SPI(1, SPI.MASTER, baudrate=200000, polarity=0, phase=0)
spi.send('hello')
spi.recv(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus
spi.send_recv('hello') # send a receive 5 bytes
I2C bus¶
from pyb import Pin, I2C
# first assign SCL and SDA to the correct pins
Pin('GP23', af=9, mode=Pin.STD_PU) # SCL
Pin('GP24', af=9, mode=Pin.STD_PU) # SDA
# configure the I2C bus
i2c = I2C(1, I2C.MASTER, baudrate=100000)
i2c.scan() # returns list of slave addresses
i2c.send('hello', 0x42) # send 5 bytes to slave with address 0x42
i2c.recv(5, 0x42) # receive 5 bytes from slave
i2c.mem_read(2, 0x42, 0x10) # read 2 bytes from slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10
i2c.mem_write('xy', 0x42, 0x10) # write 2 bytes to slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10
Watchdog timer (WDT)¶
See pyb.WDT.
from pyb import WDT
# enable the WDT with a timeout of 5s (1s is the minimum)
wdt = WDT(5000)
wdt.kick()
Real time clock (RTC)¶
See pyb.RTC and pyb.Sleep.
from pyb import RTC, Sleep
rtc = pyb.RTC()
rtc.datetime((2014, 5, 1, 4, 13, 0, 0, 0))
print(rtc.datetime())
def some_handler (rtc_obj):
# trigger the callback again in 30s
rtc_obj.callback(value=30000, handler=some_handler)
# create a RTC alarm that expires in 30s
rtc.callback(value=30000, handler=some_handler, wakes=Sleep.SUSPENDED)
# go into suspended mode waiting for the RTC alarm to expire and wake us up
Sleep.suspend()
SD card¶
See pyb.SD.
from pyb import SD
# SD card pins need special configuration so we pass 'em to the constructor
# data pin, data af, clock pin, clock af, cmd pin, cmd af
sd = pyb.SD('GP15', 8, 'GP10', 6, 'GP11', 6)
sd.enable()
WLAN (WiFi)¶
See network.WLAN and pyb.Sleep.
from network import WLAN
from pyb import Sleep
# configure the WLAN subsystem in station mode (the default is AP)
wifi = WLAN(WLAN.STA)
# go for fixed IP settings
wifi.ifconfig(('192.168.0.107', '255.255.255.0', '192.168.0.1', '8.8.8.8'))
wifi.scan() # scan for available netrworks
wifi.connect(ssid='mynetwork', security=2, key='mynetworkkey')
while not wifi.isconnected():
pass
print(wifi.ifconfig())
# enable wake on WLAN
wifi.callback(wakes=Sleep.SUSPENDED)
# go to sleep
Sleep.suspend()
# now, connect to the FTP or the Telnet server and the WiPy will wake-up
Sleep and power modes control¶
See pyb.Sleep.
from pyb import Sleep
Sleep.idle() # lowest sleep mode (~12mA), any interrupts wakes it up
Sleep.suspend() # everything except for WLAN is powered down (~950uA)
# wakes from Pin, RTC or WLAN
Sleep.hibernate() # deepest sleep mode, MCU starts from reset. Wakes from Pin and RTC.
Heart beat LED¶
See pyb.HeartBeat.
from pyb import HeartBeat
# disable the heart beat indication (you are free to use this LED connected to GP25)
HeartBeat().disable()
# enable the heart beat again
HeartBeat().enable()