2. Fading LEDs¶
In addition to turning LEDs on and off, it is also possible to control the brightness of an LED using Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM), a common technique for obtaining variable output from a digital pin. This allows us to fade an LED:

2.1. Components¶
You will need:
Standard 5 or 3 mm LED
100 Ohm resistor
Wires
Breadboard (optional, but makes things easier)
2.2. Connecting Things Up¶
For this tutorial, we will use the X1 pin. Connect one end of the resistor to X1, and the other end to the anode of the LED, which is the longer leg. Connect the cathode of the LED to ground.
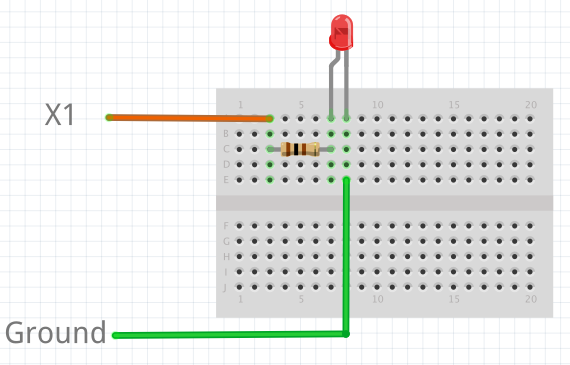
2.3. Code¶
By examining the Quick reference for the pyboard, we see that X1 is connected to channel 1 of timer 5 (TIM5 CH1). Therefore we will first create a Timer object for timer 5, then create a TimerChannel object for channel 1:
from pyb import Timer
from time import sleep
# timer 5 will be created with a frequency of 100 Hz
tim = pyb.Timer(5, freq=100)
tchannel = tim.channel(1, Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.X1, pulse_width=0)
Brightness of the LED in PWM is controlled by controlling the pulse-width, that is the amount of time the LED is on every cycle. With a timer frequency of 100 Hz, each cycle takes 0.01 second, or 10 ms.
To achieve the fading effect shown at the beginning of this tutorial, we want to set the pulse-width to a small value, then slowly increase the pulse-width to brighten the LED, and start over when we reach some maximum brightness:
# maximum and minimum pulse-width, which corresponds to maximum
# and minimum brightness
max_width = 200000
min_width = 20000
# how much to change the pulse-width by each step
wstep = 1500
cur_width = min_width
while True:
tchannel.pulse_width(cur_width)
# this determines how often we change the pulse-width. It is
# analogous to frames-per-second
sleep(0.01)
cur_width += wstep
if cur_width > max_width:
cur_width = min_width
2.4. Breathing Effect¶
If we want to have a breathing effect, where the LED fades from dim to bright then bright to dim, then we simply need to reverse the sign of wstep when we reach maximum brightness, and reverse it again at minimum brightness. To do this we modify the while loop to be:
while True:
tchannel.pulse_width(cur_width)
sleep(0.01)
cur_width += wstep
if cur_width > max_width:
cur_width = max_width
wstep *= -1
elif cur_width < min_width:
cur_width = min_width
wstep *= -1
2.5. Advanced Exercise¶
You may have noticed that the LED brightness seems to fade slowly, but increases quickly. This is because our eyes interprets brightness logarithmically (Weber’s Law ), while the LED’s brightness changes linearly, that is by the same amount each time. How do you solve this problem? (Hint: what is the opposite of the logarithmic function?)
2.6. Addendum¶
We could have also used the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to achieve the same effect. The PWM method has the advantage that it drives the LED with the same current each time, but for different lengths of time. This allows better control over the brightness, because LEDs do not necessarily exhibit a linear relationship between the driving current and brightness.