Quick reference for the Kookaberry¶
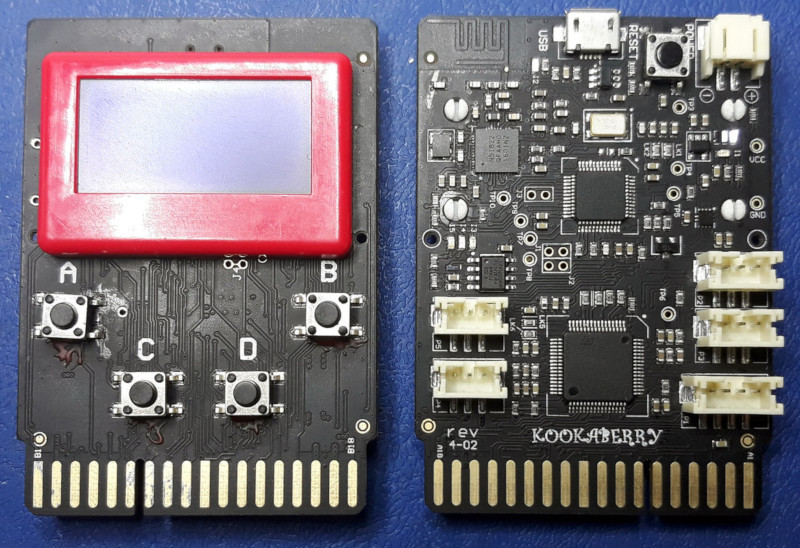
This is a quick reference for the Kookaberry. For further details see the documentation on the Kookaberry-specific modules just below.
Internal LEDs¶
See kooka.LED.
import kooka
kooka.led_red.on()
kooka.led_green.toggle()
kooka.led_green.off()
Internal buttons¶
See kooka.Button.
import kooka
print(kooka.button_a.is_pressed())
print(kooka.button_a.was_pressed())
Internal display¶
See sh1106.SH1106_SPI.
from kooka import display
display.print('hello', 123) # print objects to the display directly
display.contrast(255) # set maximum contrast
display.invert(True) # invert all pixels
display.fill(0) # clear the display
display.line(4, 5, 60, 40, 1) # draw a line
display.show() # show the frame buffer to the display
Internal accelerometer¶
See lsm303.LSM303C_Accel.
from kooka import accel
print(accel.get_xyz()) # get and print the x/y/z acceleration values
Internal compass¶
See lsm303.LSM303C_Mag.
from kooka import compass
print(compass.get_xyz()) # get and print the x/y/z magnetic values
print(compass.get_strength()) # get and print the magnetic field strength
Internal radio¶
See nrf51.Radio.
from kooka import radio
radio.enable() # enable the radio
radio.config(power=7) # set maximum power
radio.send('hello') # send a message
print(radio.receive()) # retrieve any messages on the queue
Delay and timing¶
Use the time module:
import time
time.sleep(1) # sleep for 1 second
time.sleep_ms(500) # sleep for 500 milliseconds
time.sleep_us(10) # sleep for 10 microseconds
start = time.ticks_ms() # get value of millisecond counter
delta = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start) # compute time difference
Pins and GPIO¶
See machine.Pin.
from machine import Pin
p_out = Pin('P2', Pin.OUT) # create a Pin object, in output mode
p_out.high() # set the pin high
p_out.low() # set the pin low
p_in = Pin('P3', Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP) # input mode with pull-up resistor
p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1
Timers¶
See pyb.Timer.
from machine import Timer
tim = Timer(3, freq=1000) # create Timer 3, running at 1000Hz
tim.freq(1) # change frequency to 1 Hz
# toggle an LED at the frequency of the timer
tim.callback(lambda t: kooka.led_green.toggle())
RTC (real time clock)¶
See pyb.RTC
from machine import RTC
rtc = RTC() # access the RTC
rtc.datetime((2017, 8, 23, 1, 12, 48, 0, 0)) # set a specific date and time
print(rtc.datetime()) # get date and time
PWM (pulse width modulation)¶
See machine.PWM.
from machine import PWM
pwm = PWM('P2') # create PWM object on connector P2
pwm.freq(1000) # set PWM frequency to 100Hz
pwm.duty(50) # set duty to 50%
ADC (analog to digital conversion)¶
See pyb.ADC.
from machine import ADC
adc = ADC('P4') # create ADC object on connector P4
print(adc.read()) # read value, in range 0-4095
DAC (digital to analog conversion)¶
See pyb.DAC.
from machine import DAC
dac = DAC('P4') # create DAC object on connector P4
dac.write(120) # output value, in range 0-255
UART serial bus¶
See machine.UART.
from machine import UART
uart = UART(6, 9600) # create UART 6 with baudrate 9600
uart.write('hello') # write 5 bytes
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes
I2C bus¶
See machine.I2C.
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C('P1') # construct an I2C bus on connector P1
i2c.readfrom(0x3a, 4) # read 4 bytes from slave device with address 0x3a
i2c.writeto(0x3a, '12') # write '12' to slave device with address 0x3a
buf = bytearray(10) # create a buffer with 10 bytes
i2c.writeto(0x3a, buf) # write the given buffer to the slave
SPI bus¶
See machine.SPI.
from machine import SPI
spi = SPI('DISP') # access the SPI bus connected to the display
spi.read(10) # read 10 bytes on MISO
spi.read(10, 0xff) # read 10 bytes while writing 0xff on MOSI
spi.write(b'12345') # write 5 bytes on MOSI
buf = bytearray(4) # create a buffer
spi.write_readinto(b'1234', buf) # write to MOSI and read from MISO into the buffer
Servo control¶
See kooka.Servo.
from kooka import Servo
s1 = Servo('P2') # servo on connector P2
s1.angle(45) # move to 45 degrees
s1.angle(-60, 1500) # move to -60 degrees in 1500ms
s1.speed(50) # for continuous rotation servos